What Are Knowledge Graphs?
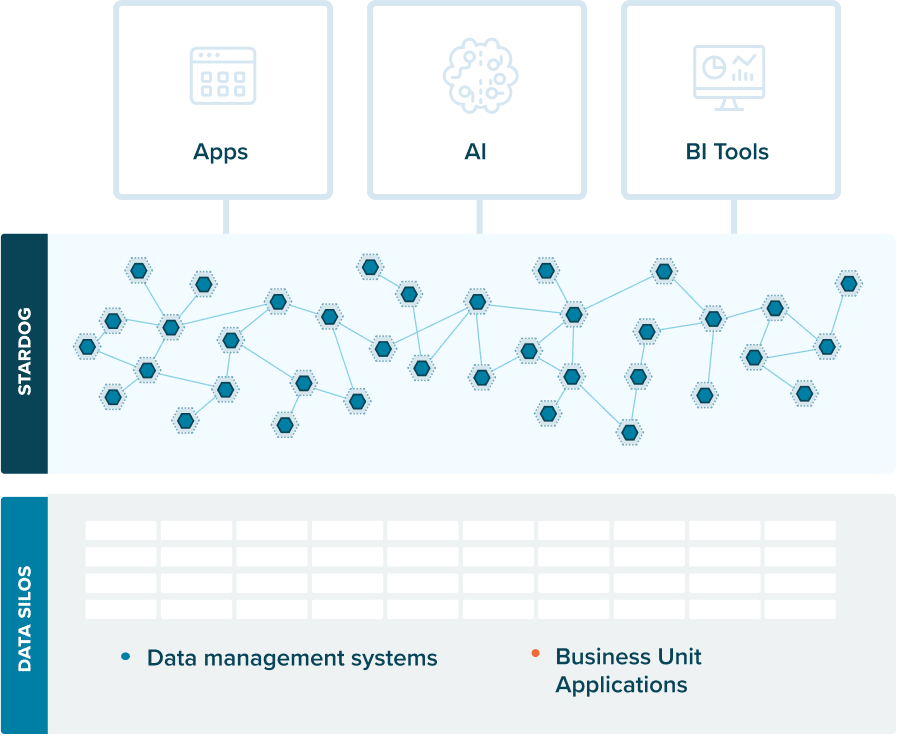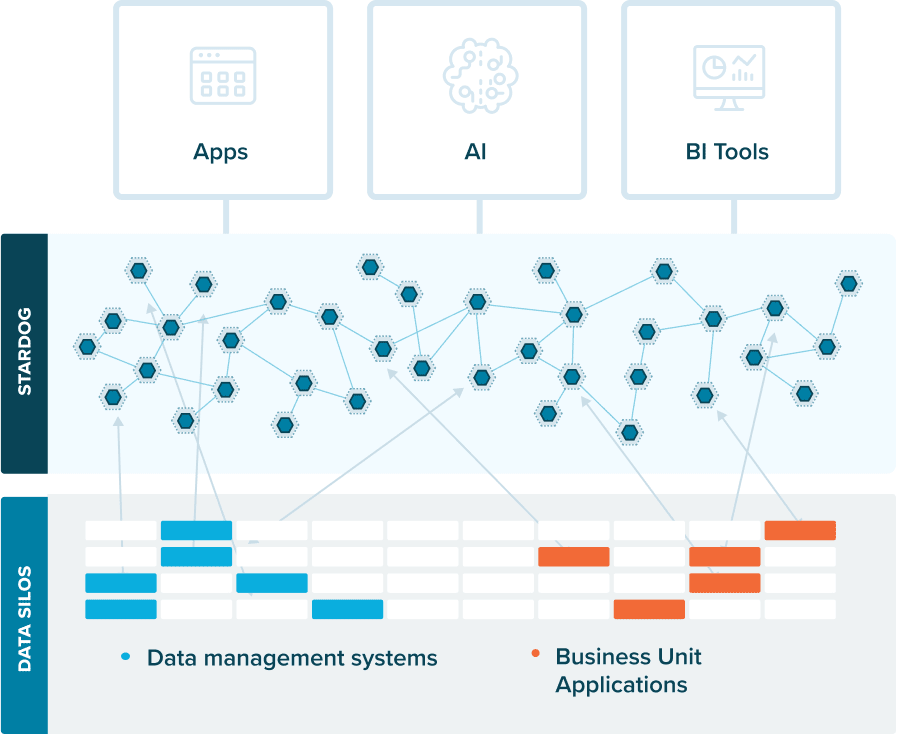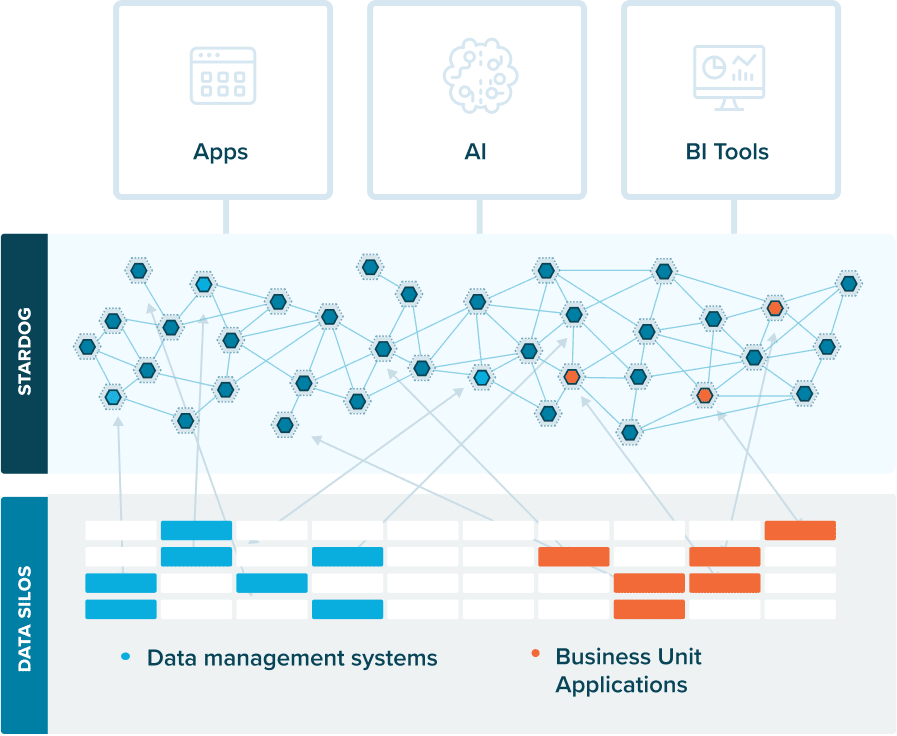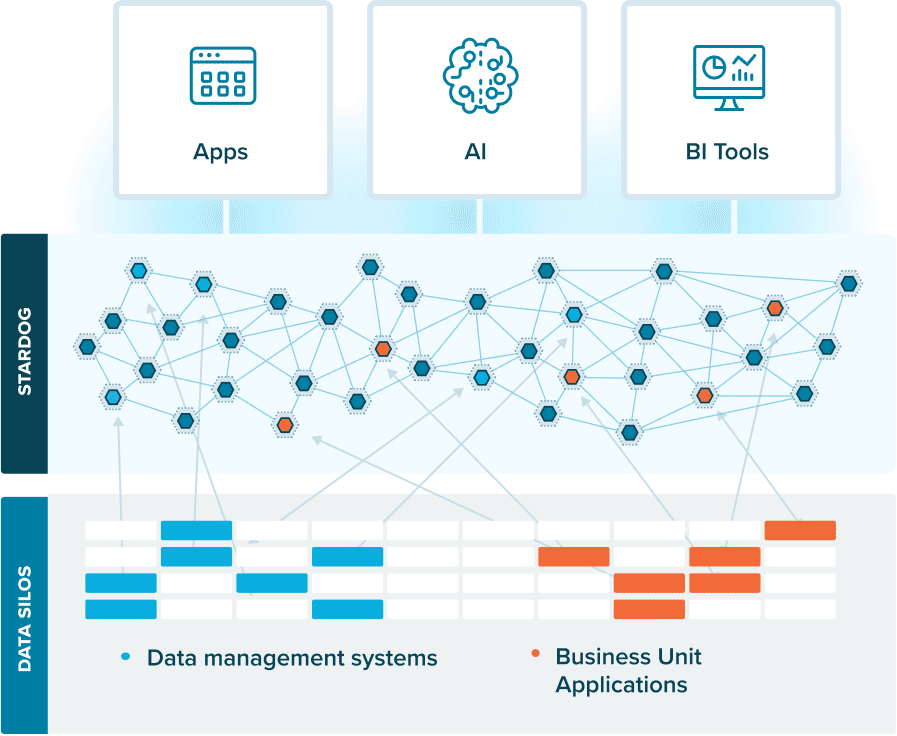
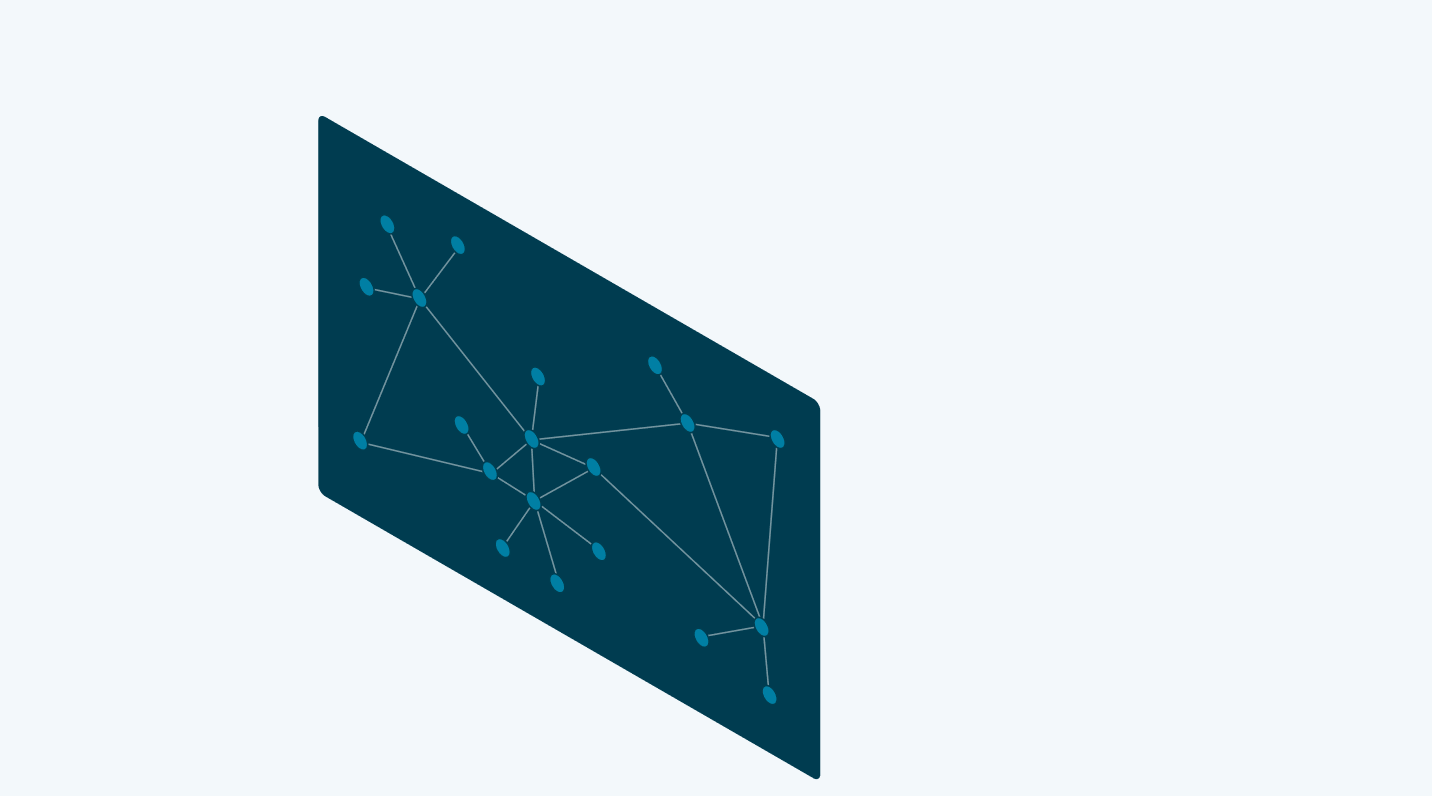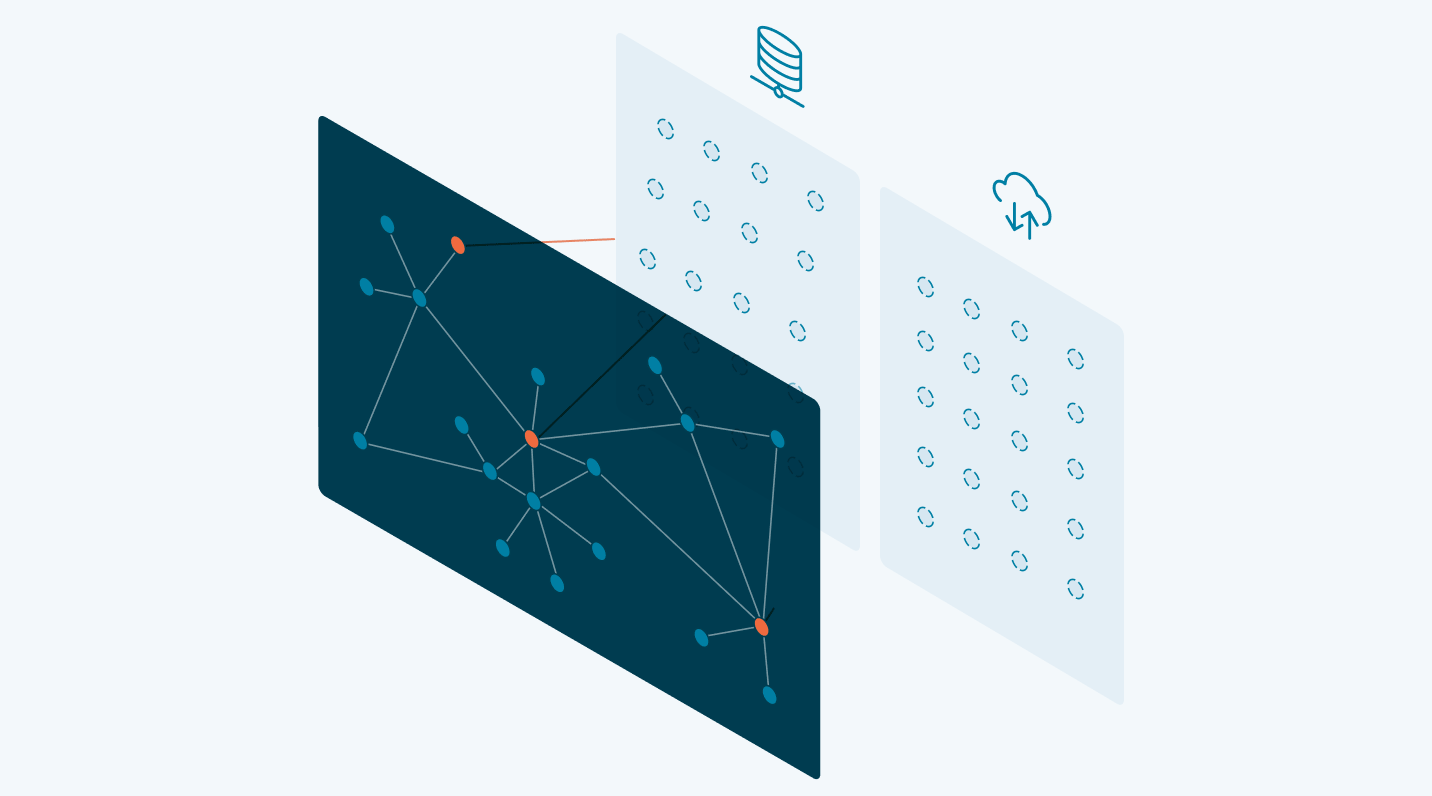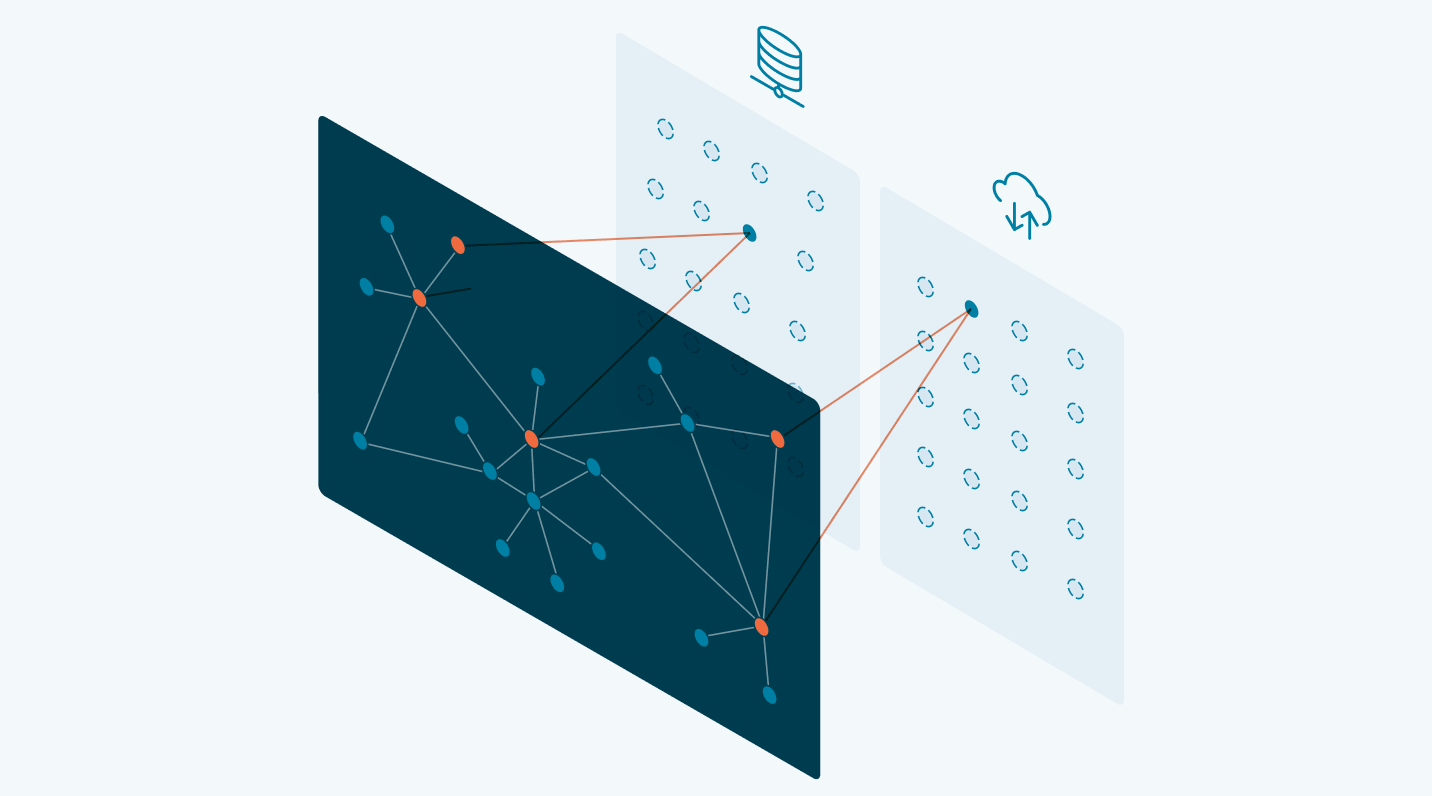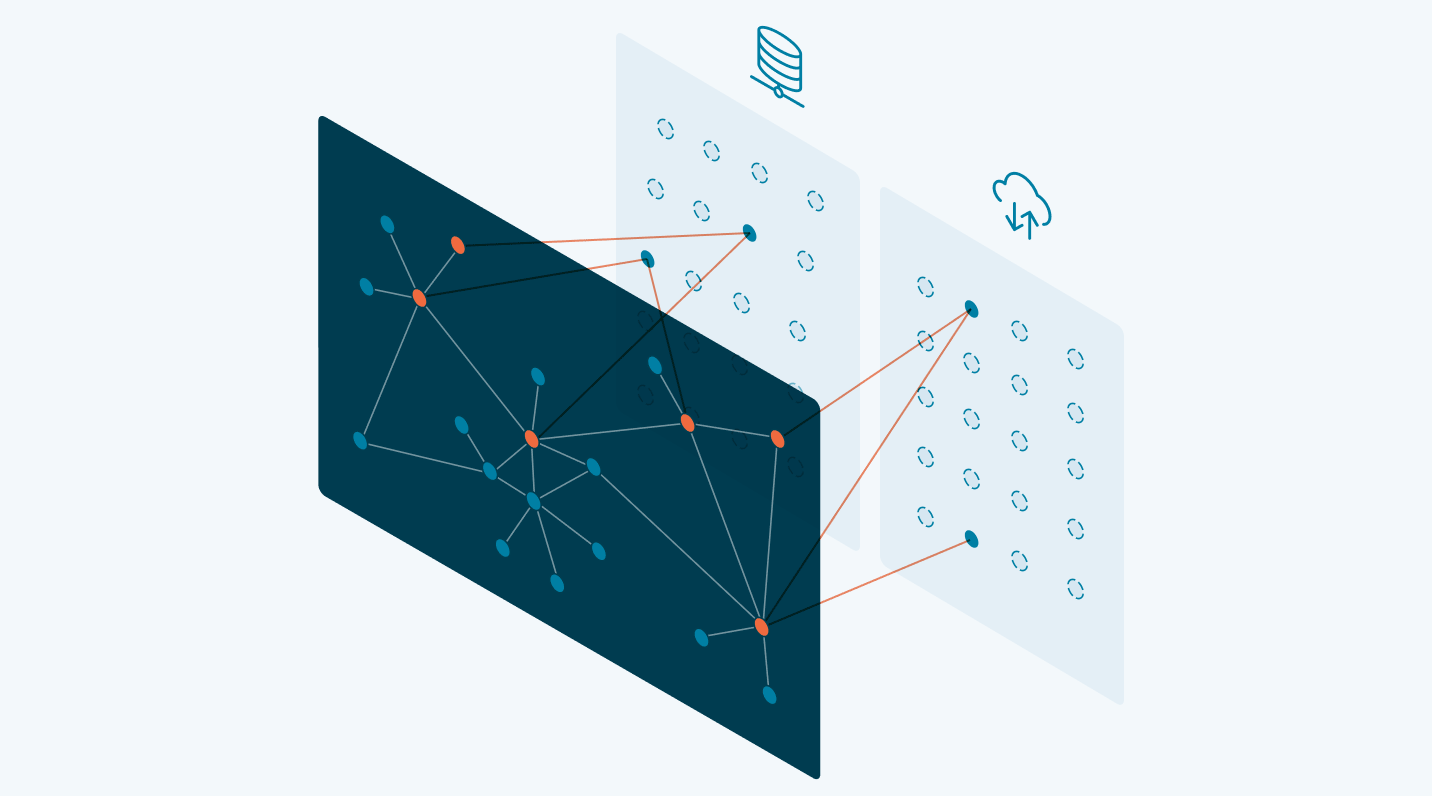
A knowledge graph is a flexible, reusable data layer used for answering complex queries. It creates connectedness with contextualized data, represented and organized in the form of graphs. Built to capture the ever-changing nature of knowledge, they easily accept new data, definitions, and requirements. An enterprise knowledge graph is simply a knowledge graph of enterprise data.
Alone, data systems are good at storing records, but bad at showing how those records relate. They can tell you what happened, but not how it connects. That’s where knowledge graphs come in.
Think about how your business understands customers. A customer isn’t just a name in a CRM. They’re tied to purchases, regions, preferences, support tickets, and dozens of other touchpoints. A knowledge graph brings those connections together, building a view that looks a lot more like real life.